In the last few years, we are facing a revolution in the SATCOM market. Mainly, it is due to the rapid development of the software-defined or even completely digital payloads. These modern satellites permit the provision of new services, while creating new necessities never imagined before. The revolution has started. Traditional payloads, understood as ad hoc hardware designed for a specific mission, have been left behind. Now, it is the time for generic solutions, based on their reconfigurable software-based counterparts, ready for dynamic demands.
The inflection point in the commercial SATCOM history can be set as 2021, when the Eutelsat operator launches Eutelsat Quantum satellite. Quantum is the first commercial satellite completely controlled by software, and capable of providing their final users with the control of its payload. Payload-as-a-service is then introduced as a new revolutionary concept. Due to the success, Eutelsat continues increasing its fleet with new satellites, boarding state-of-the-art flexible payloads.
The evolution of these payloads implies two important consequences. On the one hand, the operator is provided with almost endless possibilities to reconfigure them. On the other hand, the difficulty to manage such complex payloads will impact on the manner the operator used to manage them.
Dynamic demand, resilience systems, real-time, multi-mission, 5G/6G… How can an operator manage these complex systems in such a changing environment? Relentlessly, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are our best allies.
In this line, ATRIA project aims to apply the AI/ML techniques to relevant SATCOM use cases, selected by the experienced operators from Eutelsat, to ease and, eventually, automate their operations. To do so, GMV -with the role of Consortium coordinator and system integrator- has developed a system prototype called AI-PCS. Among others, AI-PCS integrates the AI/ML modules developed by CTTC and AIKO, the Consortium AI experts.
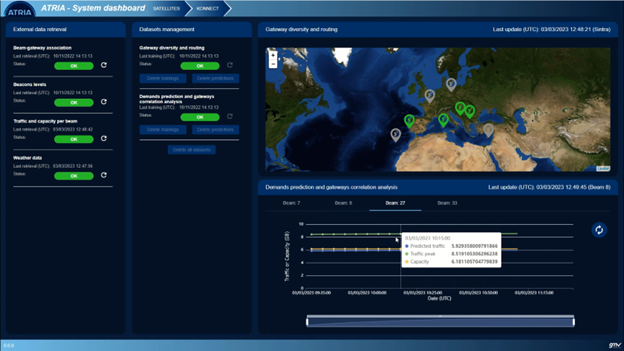
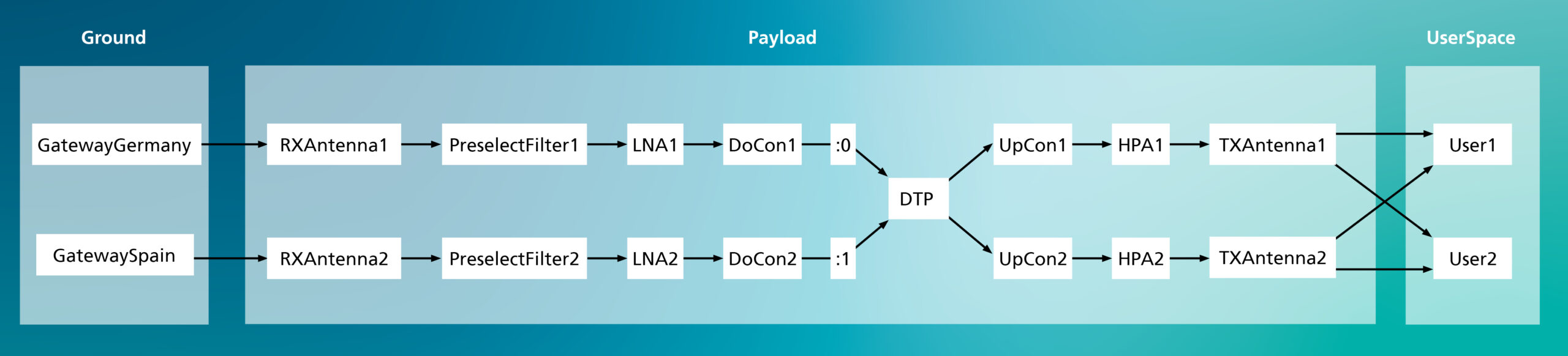
The first use case to be tackled has been the gateway diversity problem. AI-PCS has been trained to predict when it would be necessary to perform a switch operation between nominal and redundant gateways, minimizing the downtime. To do so, the AI/ML modules integrated in AI-PCS can analyze the correlation between the rainfall quantity and the beacon signals levels at the gateway locations. Then, taking as input the weather forecast, AI-PCS can predict in real-time if the switch operation is needed.
A second use case is focused on the beams. In this case, the AI/ML modules are trained with traffic and capacity data per beam from former provided services. This is of use when it comes to predict the traffic congestion per beam, and consequently warn the operator.
The AI-PCS system has been validated in an operational environment, retrieving real-time data from the operator’s data lakes (Skylogic), as well as weather forecasts from third-party systems. The AI/ML modules have provided real-time results which have been depicted in the different AI-PCS displays for their operator easy interpretation. In addition to this, AI-PCS has been provided with an alarms’ system, able to beep in case any of the exploited use cases provides a result which may imply the operator intervention. These successful results during the On-Site Acceptance Test (OSAT) execution, taken place in March 2023, have been a great push for the development of the second phase of the project. In this phase, new use cases will be supported, as well as the integration of additional developments from the rest of the Consortium partners.